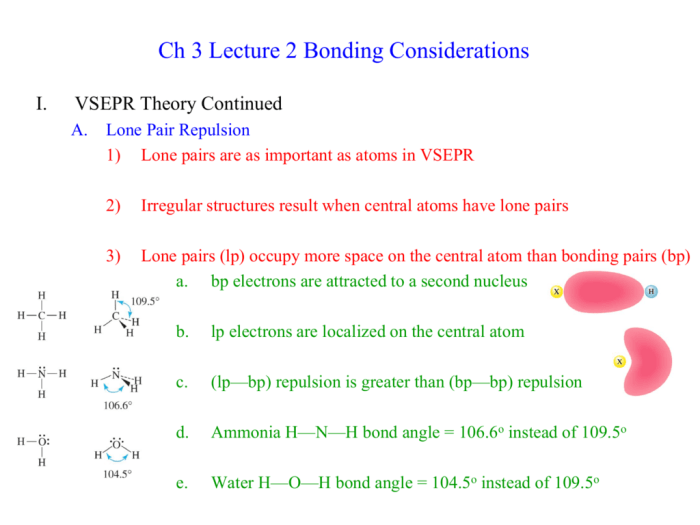
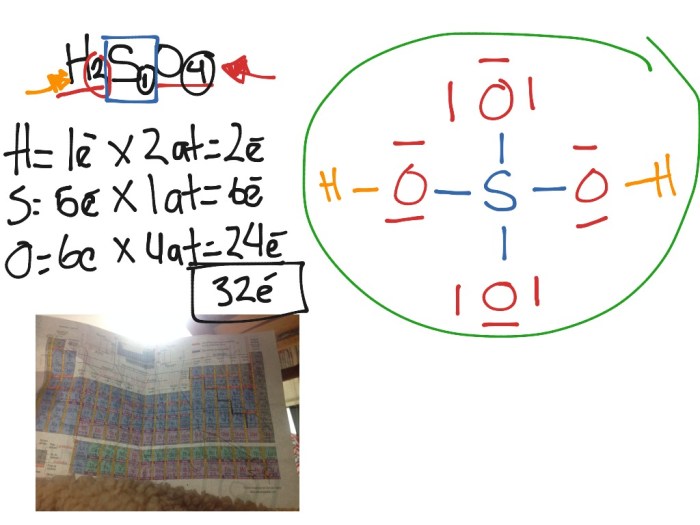
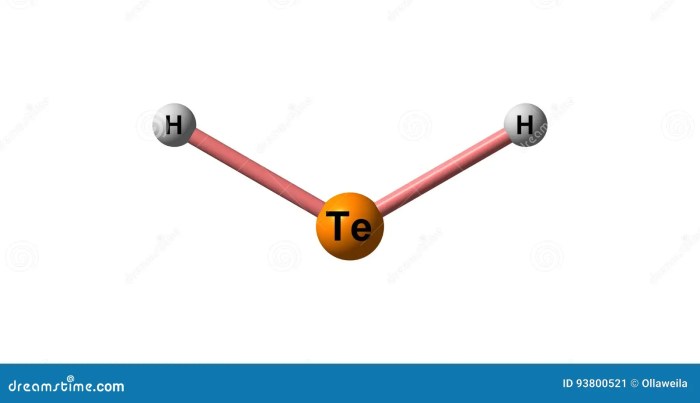
Write the chemical formula for dihydrogen monotelluride, H2Te, and delve into its fascinating world of chemistry. Discover its IUPAC nomenclature, physical and chemical properties, production methods, industrial applications, reactivity, and safety considerations.
Dihydrogen monotelluride, a remarkable compound with unique characteristics, awaits your exploration.
Chemical Formula of Dihydrogen Monotelluride
Dihydrogen monotelluride, also known as tellurium hydride, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H2Te. It is a colorless, toxic gas with a pungent odor. The IUPAC nomenclature for dihydrogen monotelluride is tellurium(II) hydride.
Properties of Dihydrogen Monotelluride
Physical Properties, Write the chemical formula for dihydrogen monotelluride
Dihydrogen monotelluride is a colorless, toxic gas with a pungent odor. It is denser than air and has a boiling point of
- 2.2 °C and a melting point of
- 49.7 °C.
Chemical Properties
Dihydrogen monotelluride is a reactive compound that can react with a variety of other compounds. It is a reducing agent and can react with oxidizing agents to form tellurium and water. It can also react with acids to form tellurium salts.
Production of Dihydrogen Monotelluride: Write The Chemical Formula For Dihydrogen Monotelluride
Dihydrogen monotelluride can be produced by a variety of methods, including:
- The reaction of tellurium with hydrogen gas
- The reaction of tellurium dioxide with hydrogen gas
- The reaction of tellurium tetrachloride with hydrogen gas
Dihydrogen monotelluride is used in a variety of industrial applications, including:
- The production of semiconductors
- The production of glass
- The production of batteries
Reactions of Dihydrogen Monotelluride

Dihydrogen monotelluride is a reactive compound that can react with a variety of other compounds. Some of the reactions of dihydrogen monotelluride include:
- Reaction with oxygen to form tellurium dioxide and water
- Reaction with chlorine to form tellurium tetrachloride and hydrogen chloride
- Reaction with sulfur to form tellurium sulfide and hydrogen sulfide
Safety Considerations for Dihydrogen Monotelluride
Dihydrogen monotelluride is a toxic gas that can cause a variety of health effects, including:
- Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Death
It is important to take precautions when handling dihydrogen monotelluride, including:
- Working in a well-ventilated area
- Wearing a respirator
- Wearing gloves
- Storing dihydrogen monotelluride in a cool, dry place
FAQ
What is the molecular weight of dihydrogen monotelluride?
129.63 g/mol
Is dihydrogen monotelluride toxic?
Yes, dihydrogen monotelluride is toxic and can cause respiratory irritation, nausea, and dizziness.