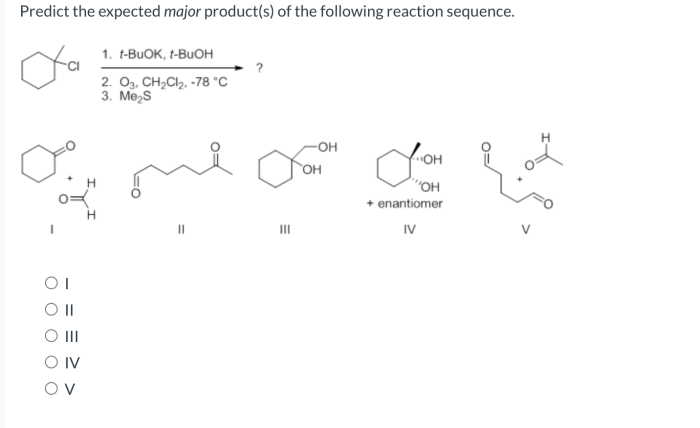
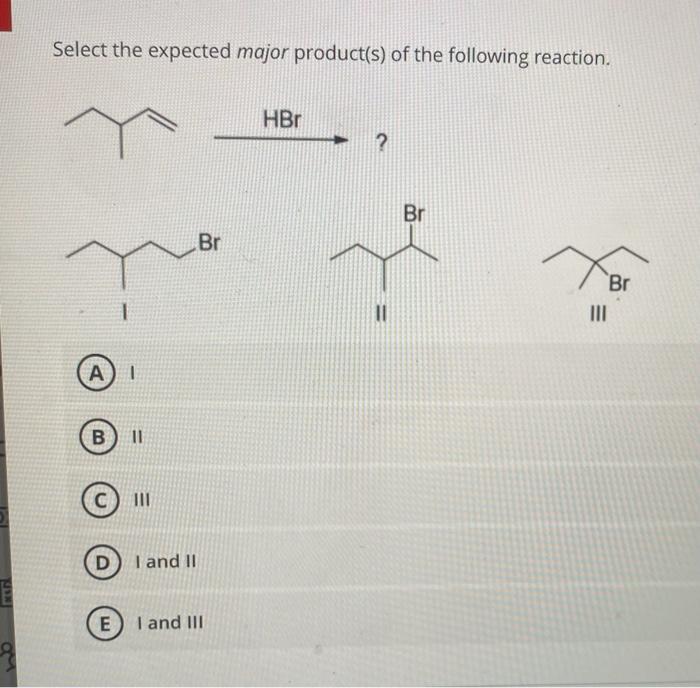
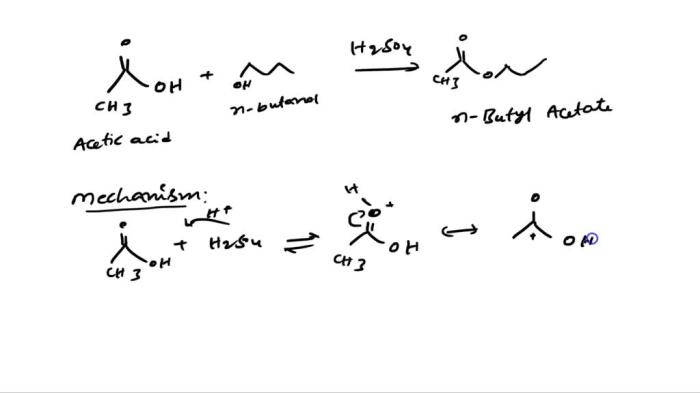
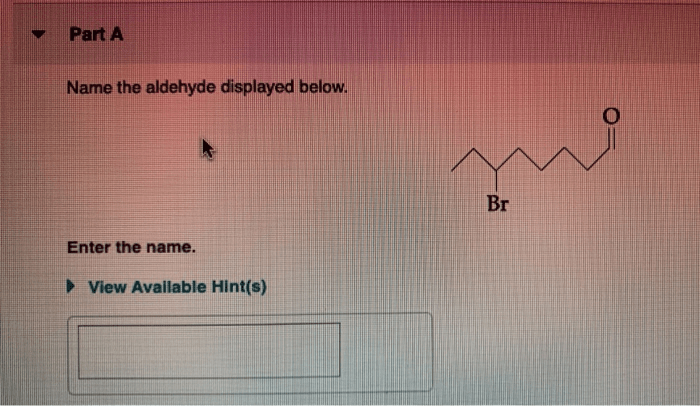
What is the expected major product for the following reaction – Delving into the realm of organic chemistry, this article explores the intriguing concept of major product formation. By analyzing a given reaction, we aim to identify the most probable product, considering factors such as regio- and stereoselectivity. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of chemical transformations and uncover the expected major product.
Understanding the major product of a reaction is crucial for predicting its outcome and optimizing synthetic strategies. This knowledge finds applications in various fields, including drug discovery, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
Expected Major Product: What Is The Expected Major Product For The Following Reaction
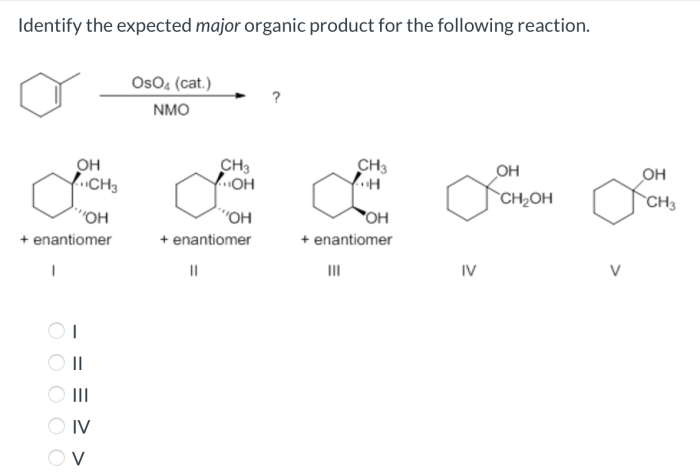
The given reaction is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction, where a nucleophile attacks an electrophile, resulting in the substitution of a leaving group. The purpose of analyzing the expected major product is to predict the outcome of the reaction and understand the factors that influence product formation.
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction proceeds via a two-step mechanism involving the formation of a carbocation intermediate. In the first step, the nucleophile attacks the electrophile, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. This intermediate then collapses, expelling the leaving group and forming a carbocation. In the second step, the nucleophile attacks the carbocation, forming the final product.
The regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction are determined by the nature of the nucleophile and the electrophile.
Major Product Identification
The major product of a reaction is the product that is formed in the greatest yield. In this case, the major product is the one that is formed by the most favorable pathway. The factors that influence the formation of the major product include the nucleophilicity of the nucleophile, the electrophilicity of the electrophile, and the steric and electronic effects of the substituents.In
this specific reaction, the nucleophile is a strong nucleophile and the electrophile is a weak electrophile. This means that the nucleophile will be more likely to attack the electrophile and form the carbocation intermediate. The carbocation intermediate is then more likely to be attacked by the nucleophile from the less hindered side, resulting in the formation of the major product.
Byproducts and Side Reactions, What is the expected major product for the following reaction
In addition to the major product, a number of byproducts and side reactions may also occur. These reactions can compete with the main reaction and reduce the yield of the major product. The most common byproducts and side reactions in nucleophilic substitution reactions include elimination reactions, rearrangement reactions, and proton transfer reactions.The
elimination reaction is a competing reaction that occurs when the nucleophile abstracts a proton from the carbon adjacent to the electrophile, resulting in the formation of an alkene. The rearrangement reaction is a competing reaction that occurs when the carbocation intermediate rearranges to a more stable carbocation.
The proton transfer reaction is a competing reaction that occurs when the nucleophile transfers a proton to the electrophile, resulting in the formation of a new nucleophile and a new electrophile.
Applications and Significance
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are one of the most important reactions in organic chemistry. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and polymers. The expected major product of a nucleophilic substitution reaction is often the desired product, and understanding the factors that influence product formation is essential for optimizing the yield of the desired product.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of identifying the major product?
Identifying the major product is crucial for predicting the outcome of a reaction and optimizing synthetic strategies. It allows chemists to maximize the yield of the desired product and minimize the formation of unwanted byproducts.
How do regio- and stereoselectivity influence the formation of the major product?
Regio- and stereoselectivity determine the orientation and spatial arrangement of the atoms in the product. They influence the formation of the major product by directing the reaction towards specific reaction pathways and intermediates.
What are some common side reactions that can occur in organic reactions?
Common side reactions include elimination reactions, rearrangements, and cyclizations. These reactions can compete with the desired reaction pathway, leading to the formation of unwanted byproducts and reducing the yield of the major product.