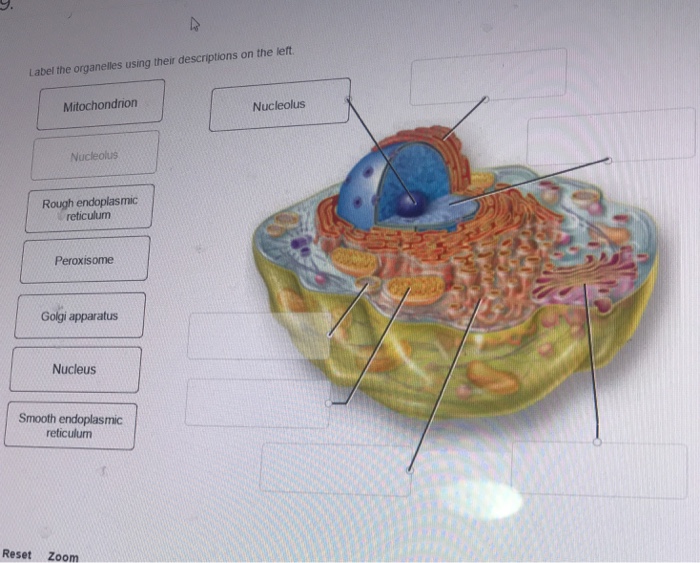
Label the organelles using their descriptions on the left. – In the realm of scientific research, accurately labeling organelles is of paramount importance. This detailed guide, “Label the Organelles Using Their Descriptions on the Left,” provides a comprehensive overview of the methods, criteria, and applications involved in this essential aspect of biological investigation.
Organelle labeling enables researchers to visualize, identify, and study the diverse structures within cells. It plays a crucial role in cell biology, developmental biology, and pathology, contributing to advancements in our understanding of cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
1. Organelle Identification
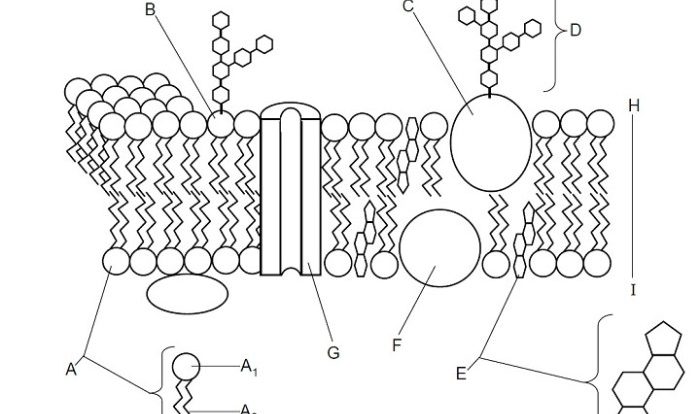
Labeling organelles is crucial for understanding their functions and cellular organization. Organelles are subcellular structures that perform specific tasks essential for cell function. By labeling organelles, researchers can visualize their location, structure, and dynamics, providing insights into cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
Examples of organelles include:
- Mitochondria:Energy production
- Ribosomes:Protein synthesis
- Golgi apparatus:Protein modification and secretion
- Lysosomes:Cellular waste disposal
- Endoplasmic reticulum:Protein folding and transport
Accurate labeling of organelles is vital for scientific research as it enables researchers to:
- Study the structure and function of organelles
- Track organelles in real-time
- Identify and characterize organelles in different cell types and tissues
- Understand the role of organelles in cellular processes and disease
2. Methods for Labeling Organelles
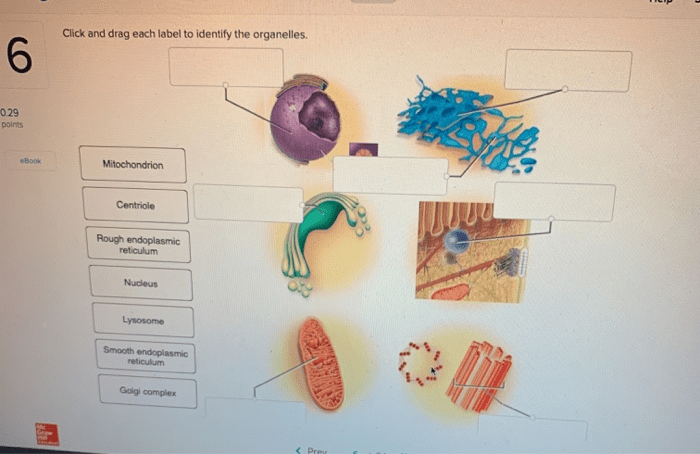
Various methods are used to label organelles, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Immunofluorescence:Uses antibodies to bind to specific proteins on the organelle surface, which are then visualized using fluorescent dyes.
- Electron microscopy:Uses high-energy electrons to visualize the ultrastructure of organelles, including their internal components.
- In situ hybridization:Uses fluorescently labeled probes to bind to specific RNA sequences within organelles, allowing for their localization and identification.
Step-by-step protocol for immunofluorescence labeling:
- Fix cells to preserve their structure.
- Permeabilize cells to allow antibodies to enter.
- Block nonspecific antibody binding.
- Incubate cells with primary antibody specific to the target organelle.
- Wash away unbound primary antibody.
- Incubate cells with fluorescently labeled secondary antibody that binds to the primary antibody.
- Wash away unbound secondary antibody.
- Visualize fluorescently labeled organelles using a microscope.
3. Creating Organelle Labels
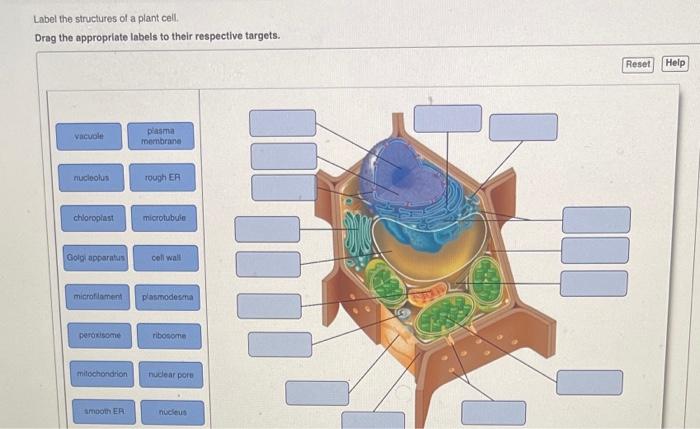
Effective organelle labels are clear, informative, and standardized to ensure consistency and accuracy in scientific communication.
Criteria for creating organelle labels:
- Accuracy:Labels should accurately represent the identity and function of the organelle.
- Consistency:Labels should be consistent across different research studies and publications.
- Simplicity:Labels should be brief and easy to understand.
- Informative:Labels should provide relevant information about the organelle, such as its function and location.
Examples of well-labeled organelles:
- Mitochondria (mt)
- Ribosomes (r)
- Golgi apparatus (GA)
- Lysosomes (Ly)
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Table to organize and display organelle labels:
| Organelle | Abbreviation | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Mitochondria | mt | Energy production |
| Ribosomes | r | Protein synthesis |
| Golgi apparatus | GA | Protein modification and secretion |
| Lysosomes | Ly | Cellular waste disposal |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | ER | Protein folding and transport |
4. Applications of Organelle Labeling: Label The Organelles Using Their Descriptions On The Left.
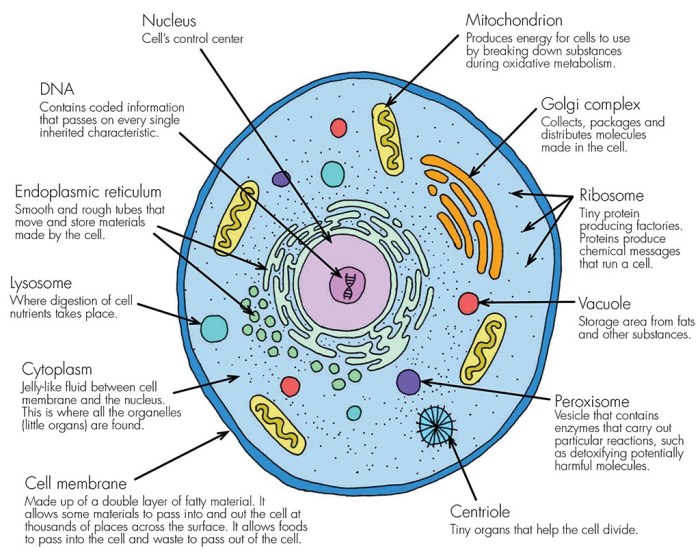
Organelle labeling is a versatile tool used in various fields of biology:
- Cell biology:Studying the structure, function, and dynamics of organelles within cells.
- Developmental biology:Investigating the role of organelles in embryonic development and tissue differentiation.
- Pathology:Identifying and characterizing organelles in diseased cells to understand disease mechanisms.
Examples of research studies using organelle labeling:
- Immunofluorescence labeling of mitochondria in neuronsto study mitochondrial dynamics during neurodegenerative diseases.
- Electron microscopy of ribosomes in bacteriato investigate the structural changes associated with antibiotic resistance.
- In situ hybridization of Golgi apparatus in cancer cellsto identify biomarkers for targeted therapies.
Organelle labeling has immense potential for future research in:
- Understanding the molecular mechanisms of organelle function
- Developing novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for organelle-related diseases
- Exploring the role of organelles in cellular aging and regeneration
Top FAQs
What are the key criteria for creating clear and informative organelle labels?
Clarity, accuracy, consistency, and conciseness are essential criteria for effective organelle labeling.
What are the advantages of using immunofluorescence for organelle labeling?
Immunofluorescence allows for the specific targeting of organelles using antibodies, providing high-resolution images.
How can organelle labeling contribute to research in developmental biology?
By tracking organelle dynamics during development, researchers can gain insights into cellular differentiation and morphogenesis.