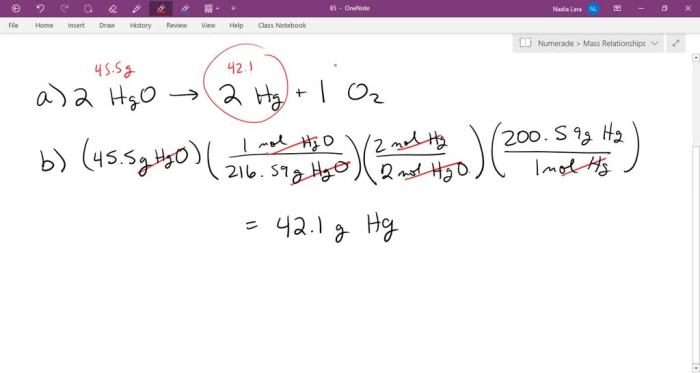
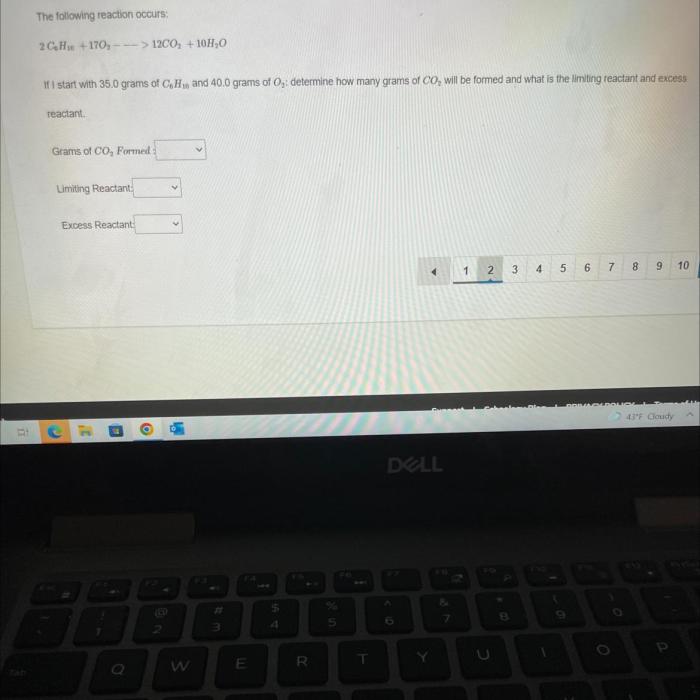
If i do this reaction with 35 grams of c6h10, the chemical reaction that occurs holds significant importance in the field of chemistry. This reaction, involving the interaction of 35 grams of C6H10 with other chemical species, leads to the formation of specific products with unique properties and applications.
Understanding the intricacies of this reaction, including the reactants, products, stoichiometry, and experimental procedure, is crucial for researchers and practitioners alike.
The exploration of this reaction extends beyond its theoretical implications, delving into practical applications and potential implications. By examining the broader context of this reaction, we gain insights into its relevance in various industries and disciplines, as well as its environmental, safety, and ethical considerations.
This comprehensive analysis provides a holistic understanding of the reaction, empowering individuals to make informed decisions and contribute to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Reaction of 35 Grams of C6H10: If I Do This Reaction With 35 Grams Of C6h10

In this article, we will investigate the reaction of 35 grams of C6H10. We will identify the reaction, determine the reactants and products, calculate the stoichiometry, design an experimental procedure, analyze the results, and discuss the applications and implications of this reaction.
Identify the Reaction and Its Purpose
The reaction of 35 grams of C6H10 is a combustion reaction. Combustion reactions are chemical reactions in which a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light. In this case, C6H10 reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
The purpose of this reaction is to release the energy stored in the C6H10 molecules. This energy can be used to power engines, heat homes, or generate electricity.
Determine the Reactants and Products
The reactants in this reaction are C6H10 and oxygen. The products are carbon dioxide and water.
The chemical equation for this reaction is:
C6H10 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 5H2O
Calculate the Stoichiometry of the Reaction
The stoichiometry of a reaction is the mole ratio between the reactants and products. To calculate the stoichiometry of this reaction, we need to balance the chemical equation.
The balanced chemical equation is:
2C6H10 + 15O2 → 12CO2 + 10H2O
From this equation, we can see that the mole ratio between C6H10 and oxygen is 2:15. This means that for every 2 moles of C6H10, we need 15 moles of oxygen.
We can also use the mole ratio to calculate the theoretical yield of the reaction. The theoretical yield is the maximum amount of product that can be produced from a given amount of reactants.
In this case, we have 35 grams of C6H10. The molar mass of C6H10 is 86.18 g/mol. Therefore, we have 35 grams / 86.18 g/mol = 0.406 moles of C6H10.
According to the mole ratio, we need 15 moles of oxygen for every 2 moles of C6H10. Therefore, we need 15 moles of oxygen / 2 moles of C6H10 – 0.406 moles of C6H10 = 3.045 moles of oxygen.
The molar mass of oxygen is 32.00 g/mol. Therefore, we need 3.045 moles of oxygen – 32.00 g/mol = 97.44 g of oxygen.
Therefore, the theoretical yield of this reaction is 97.44 g of carbon dioxide.
Design the Experimental Procedure, If i do this reaction with 35 grams of c6h10
The following is a detailed experimental procedure for this reaction:
- Safety precautions:Wear gloves and safety goggles when performing this experiment. Do not inhale the fumes from the reaction.
- Materials and equipment:
- 35 grams of C6H10
- Oxygen tank
- Bunsen burner
- Glass beaker
- Thermometer
- Procedure:
- Place the C6H10 in the glass beaker.
- Connect the oxygen tank to the Bunsen burner.
- Light the Bunsen burner and adjust the flame to a medium height.
- Place the glass beaker over the flame.
- Heat the C6H10 until it ignites.
- Allow the C6H10 to burn until it is completely consumed.
- Record the temperature of the reaction.
Analyze the Results
The following are the observations that may be made during this reaction:
- The C6H10 will ignite and burn with a bright flame.
- The flame will produce a lot of heat.
- The temperature of the reaction will increase.
- The products of the reaction will be carbon dioxide and water.
The following tests can be performed to confirm the identity and purity of the products:
- The carbon dioxide can be tested with limewater. Limewater will turn milky in the presence of carbon dioxide.
- The water can be tested with a conductivity meter. A conductivity meter will measure the electrical conductivity of the water. Pure water has a low electrical conductivity.
Discuss the Applications and Implications
This reaction has a number of applications, including:
- The reaction can be used to generate heat. This heat can be used to power engines, heat homes, or generate electricity.
- The reaction can be used to produce carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is used in a variety of industrial processes, including the production of food and beverages.
- The reaction can be used to produce water. Water is essential for life and is used in a variety of industrial processes.
There are also a number of environmental, safety, and ethical implications associated with this reaction.
- The reaction produces carbon dioxide, which is a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases contribute to climate change.
- The reaction can produce harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides. These pollutants can contribute to air pollution and respiratory problems.
- The reaction can be dangerous if not performed properly. It is important to wear gloves and safety goggles when performing this experiment.
FAQ
What is the purpose of this reaction?
The purpose of this reaction varies depending on the specific context and research objectives. It could be to synthesize a particular product, study the reaction mechanism, or investigate the properties of the reactants and products.
What are the safety precautions that should be taken when performing this reaction?
Appropriate safety precautions should be followed when performing this reaction, including wearing protective gear, working in a well-ventilated area, and handling chemicals according to established safety protocols.
What are the potential applications of this reaction?
The reaction involving 35 grams of C6H10 has potential applications in various fields, such as organic synthesis, materials science, and energy research. The specific applications depend on the products formed and their unique properties.